Interacting with data through ADAM’s evidence access layer¶
ADAM exposes access to distributed datasets of genomic data through the ADAMContext entrypoint. The ADAMContext wraps Apache Spark’s SparkContext, which tracks the configuration and state of the current running Spark application. On top of the SparkContext, the ADAMContext provides data loading functions which yield GenomicRDDs. The GenomicRDD classes provide a wrapper around Apache Spark’s two APIs for manipulating distributed datasets: the legacy Resilient Distributed Dataset (Zaharia et al. 2012) and the new Spark SQL Dataset/DataFrame API (Armbrust et al. 2015). Additionally, the GenomicRDD is enriched with genomics-specific metadata such as computational lineage and sample metadata, and optimized genomics-specific query patterns such as region joins and the auto-parallelizing pipe API for running legacy tools using Apache Spark.
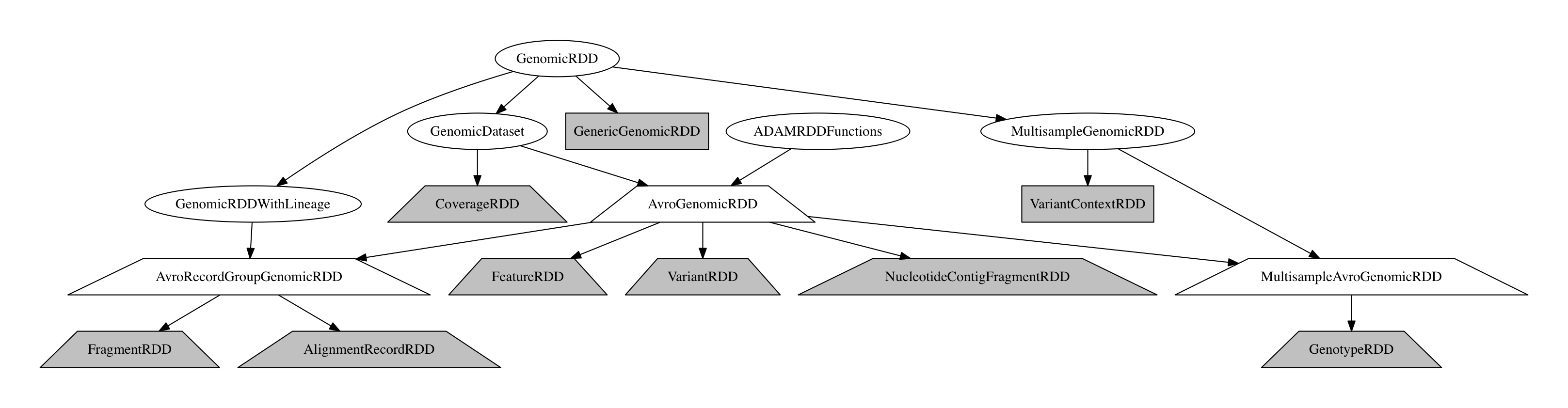
The GenomicRDD Class Hierarchy
All GenomicRDDs include a sequence dictionary which describes the reference genome that the data in the RDD are aligned to, if one is known. Additionally, RecordGroupGenomicRDD store a dictionary with read groups that are attached to the reads/fragments. Similarly, the MultisampleGenomicRDD includes a list of samples who are present in the dataset.

